Introduction
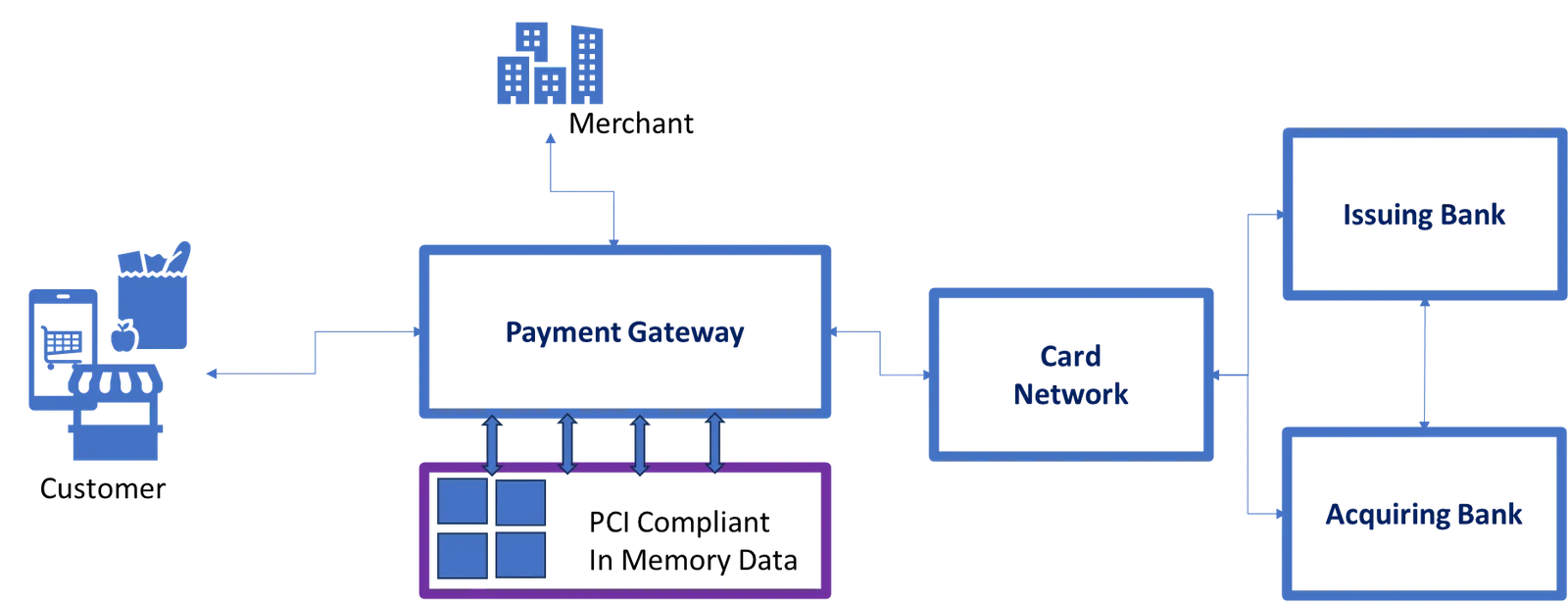
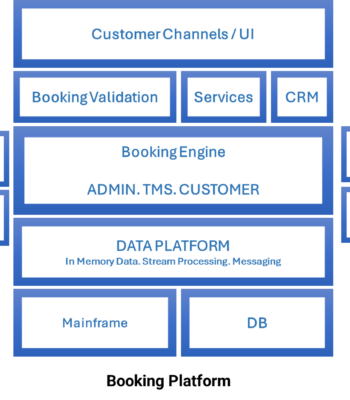
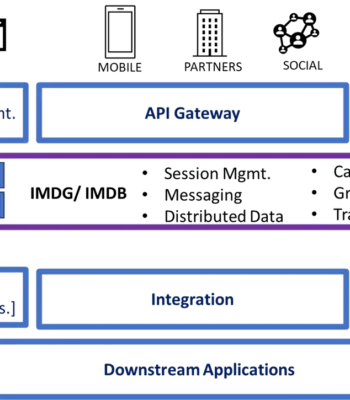
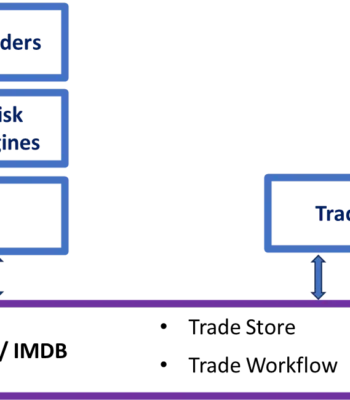
In-Memory databases can significantly enhance automated payment processing systems by improving speed, efficiency, and overall performance.
The challenge in the customer platform were improved by employing the following strategies:
Lightning-Fast Processing & High Throughput
As the data is held in RAM rather than on disk, this enables extremely fast data access. Speed is critical for processing payments in real-time or near real-time. Transactions can be processed and authorized much more quickly, reducing payment processing times and improving the overall user experience. In-Memory databases can handle high transaction throughput, making them suitable for scenarios where thousands or even millions of payments need to be processed per second, such as during peak shopping periods or financial trading
Low Latency
In-Memory databases offer low latency and near-instant response times. For automated payment processing systems, especially in scenarios where milliseconds matter (such as online retail or financial transactions), low latency is essential to ensure quick authorization and confirmations.
Scalability
In-Memory Data Grids are highly scalable and can handle large volumes of concurrent transactions. This scalability is crucial for businesses with rapidly growing transaction volumes, as it ensures that the payment processing system can handle spikes in demand without degradation in performance.
Caching Mechanisms
In-Memory Databases/Grids can act as high-performance caching layers. They can cache frequently accessed payment data, such as customer profiles or transaction history, reducing the need to fetch this data from slower external sources, like disk-based databases or external APIs.
Real-Time Analytics
In-Memory databases can support real-time analytics, allowing businesses to gain insights from transaction data as it happens. This can be invaluable for fraud detection, risk assessment and customer behaviour analysis, by enabling proactive actions in real-time.
Data Integrity and Durability
In-Memory databases frequently incorporate mechanisms to ensure data integrity and durability. Despite data primarily residing in memory, it is regularly saved to disk as a precaution against data loss in the event of a system failure. This provides both speed and data protection.
Reduced I/O Overhead
Traditional disk-based databases read and write data from and to storage devices, which can be a significant performance bottleneck. In-Memory databases eliminate much of this I/O overhead, making data access and updates almost instantaneous.
Concurrent Access: In-Memory databases are well-suited for handling concurrent access from multiple users and applications. This makes them a good fit for scenarios where multiple payment gateways, services, and devices need to interact with the payment processing system simultaneously.
Conclusion
In conclusion, In-Memory databases are an excellent choice for automated payment processing systems, particularly in situations where speed, low latency, scalability, and real-time analytics are crucial, however these need to be fine tuned appropriately for the solution in context.
By leveraging the capabilities of In-Memory databases, processing payments will be more efficient, enhance customer experiences, and allows customer to stay competitive in today’s fast-paced digital economy.
Connect with us at info@mach41.com for insights on the topics discussed in this article or to explore reviews, consulting, and solutioning services for Hazelcast and other DataGrid solutions.