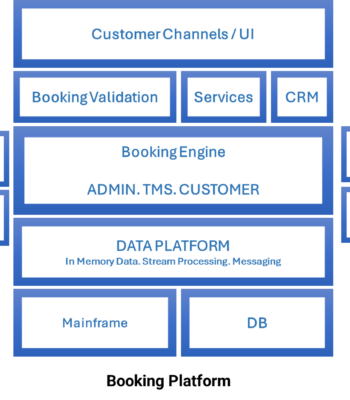
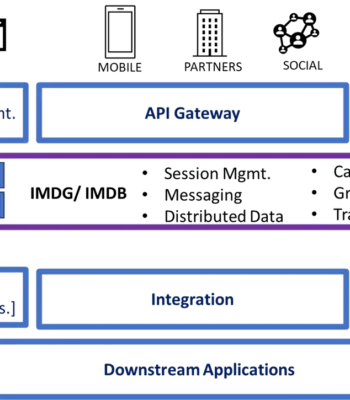
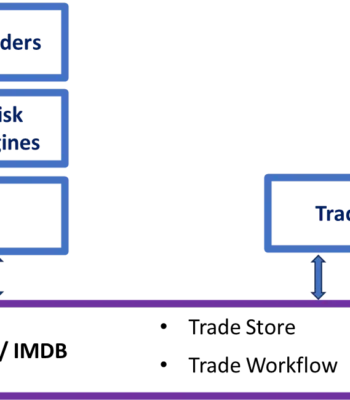
Introduction
In-Memory Data Grid/Database can significantly improve Mainframe off-load by providing speed, scalability, and cost-effectiveness in handling critical data processing tasks. Mainframe off-load refers to the process of transferring data and processing workloads from traditional mainframe systems to more modern and efficient computing environments.
Here’s how In-Memory Data Grid/Database can enhance this transition:
Cost Savings
Mainframes are known for their high operational and maintenance costs. By off-loading workloads to In-Memory Data Grid/Database, organizations can achieve cost savings by reducing mainframe-related expenses, such as licensing, hardware maintenance, and energy consumption.
Scalability
In-Memory Data Grid/Database are highly scalable, allowing them to handle growing workloads and data volumes. This scalability is critical for organizations looking to off-load mainframe workloads and ensure that their new environment can handle increased demands.
Integration with Modern Technologies
In-Memory Data Grid/Database are designed to work seamlessly with modern technologies, making it easier to integrate legacy mainframe applications with newer systems, databases, and APIs. This simplifies the process of transitioning to a more modern IT landscape.
Data Migration and Synchronization
In-Memory Data Grid/Database can help with data migration and synchronization, ensuring that data is transferred accurately and consistently between mainframes and modern systems during the off-load process
Real-Time Data Processing
In-Memory Data Grid/Database store data in RAM, allowing for rapid data retrieval and processing. This speed is crucial for handling real-time data processing workloads, which are common in mainframe systems. In-Memory Data Grids load data much faster than traditional mainframes, enabling real-time analytics and decision-making.
Latency Access
Low In-Memory Data Grid/Database offer low-latency data access, ensuring that applications can retrieve data quickly and respond to user requests with minimal delay. This is particularly important when migrating mainframe workloads to modern environments to maintain or improve performance.
Batch Processing Acceleration
Mainframes often handle batch processing tasks, such as large-scale data processing and reporting. In-Memory Data Grid/Database can accelerate these batch processing tasks, reducing the time required to complete them and improving overall efficiency.
Data Caching and Preloading
In-Memory Data Grid/Database can cache frequently accessed data, reducing the need to retrieve data from slower mainframe systems. This caching improves application performance and responsiveness.
Real-Time Analytics
In-Memory Data Grid/Database can support real-time analytics, enabling organizations to gain insights from data as it is generated. This is particularly valuable for businesses looking to make data-driven decisions in real-time.
Improved User Experience
By reducing response times and improving system performance, In-Memory Data Grid/Database contribute to a better user experience for both customers and internal users. This is especially important when off-loading mainframe systems used for customer-facing applications.
Data Archiving and Backup
In-Memory Data Grid/Database can be used for efficient data archiving and backup, preserving data from mainframes while reducing the complexity and cost of maintaining legacy systems.
Conclusion
In summary, In-Memory Data Grids/Database are instrumental in improving Mainframe off-load by offering real-time data processing, low latency, scalability, and cost-effectiveness. By off-loading mainframe workloads to modern, In-Memory Data Grids can achieve greater operational efficiency, enhanced performance, and cost savings while embracing contemporary technologies and practices.
Connect with us at info@mach41.com for insights on the topics discussed in this article or to explore reviews, consulting, and solutioning services for Hazelcast and other DataGrid solutions.